BASIN ANALYSIS
May 27, 2010
Sedimentary basin analysis is a geologic method by which the history of a sedimentary basin is revealed, by analyzing the sediment fill itself. Aspects of the sediment, namely its composition, primary structures, and internal architecture, can be synthesized into a history of the basin fill. Such a synthesis can reveal how the basin formed, how the sediment fill was transported or precipitated, and reveal sources of the sediment fill. From such syntheses models can be developed to explain broad basin formation mechanisms. Examples of such basinal environments include backarc, forearc, passive margin, epicontinental, and extensional basins.
Sedimentary basin analysis is largely conducted by two types of geologists who have slightly different goals and approaches. The petroleum geologist, whose the ultimate goal is to determine the possible presence and extent of hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon-bearing rocks in a basin, and the academic geologist, who may be concerned with any or all facets of a basin's evolution. Petroleum industry basin analysis is often conducted on subterranean basins through the use of reflection seismology and data from well logging. Academic geologists study subterranean basins as well as those basins which have been exhumed and dissected by subsequent tectonic events. Thus academics sometimes use petroleum industry techniques, but in many cases they are able to study rocks at the surface. Techniques used to study surficial sedimentary rocks include: measuring stratigraphic sections, identifying sedimentary depositional environments and constructing a geologic map.
An important tool in sedimentary basin analysis is sequence stratigraphy, in which various sedimentary sequences are related to pervasive changes in sea level and sediment supply.
Basin modelling is the term broadly applied to a group of geological disciplines that can be used to analyse the formation and evolution of sedimentary basins, often but not exclusively to aid evaluation of potential hydrocarbon reserves.
At its most basic, a basin modelling exercise must assess:
- The burial history of the basin (see back-stripping).
- The thermal history of the basin (see thermal history modelling).
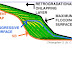
- The maturity history of the source rocks.
- The expulsion, migration and trapping of hydrocarbons.
By doing so, valuable inferences can be made about such matters as hydrocarbon generation and timing, maturity of potential source rocks and migration paths of expelled hydrocarbons.











0 comments:
Post a Comment